Everyone overcomplicates learning Python automation. They pile up dozens of tutorials, jump between frameworks, and spend months on theory before writing useful code. Then they burn out, convinced Python is harder than it looks.
Here’s what actually works: focused learning, immediate application, and skipping everything you don’t need right now. Python automation is genuinely one of the most accessible programming skills — if you approach it correctly. This guide shows you the simple path from complete beginner to automating real tasks. For step-by-step technical coverage, this complete Python automation guide walks you through everything in detail.
Why Python Automation Is Easier Than You Think
Let’s address the elephant in the room: yes, you can learn this. Python isn’t like other programming languages that require computer science backgrounds. It was literally designed to be readable and beginner-friendly.
Python reads like English. Look at this code:
for file in folder:
if file.endswith('.csv'):
process(file)
Even without programming experience, you probably understood that: go through files in a folder, and if a file ends with .csv, process it. That’s Python — logic expressed in near-English.
Automation requires a small subset of Python. You don’t need to learn everything. Data scientists use different Python features than web developers. For automation specifically, you need about 20% of Python’s capabilities — and that 20% handles 90% of automation tasks.
Libraries do the heavy lifting. Want to read Excel files? One line of code. Send emails? Five lines. Scrape a website? Ten lines. Python’s ecosystem of libraries means you’re assembling solutions from pre-built pieces, not creating everything from scratch.
The Realistic Timeline
Forget “learn Python in a weekend” promises. Here’s what honest progress looks like:
Week 1-2: Python basics click into place. Variables, loops, conditions, functions. You write small scripts that actually run.
Week 3-4: File operations become natural. Reading, writing, organizing files with code feels powerful.
Week 5-6: You automate your first real task. Something from actual work or life that used to take 30 minutes now takes 30 seconds.
Week 7-8: Confidence builds. You see automation opportunities everywhere. New challenges feel solvable, not scary.
Month 3+: You’re building increasingly complex automations. APIs, databases, scheduled tasks — each new skill multiplies what you can do.
Most people can automate meaningful tasks within their first month of consistent learning. Not mastery — that takes longer — but genuine, useful automation that saves real time.
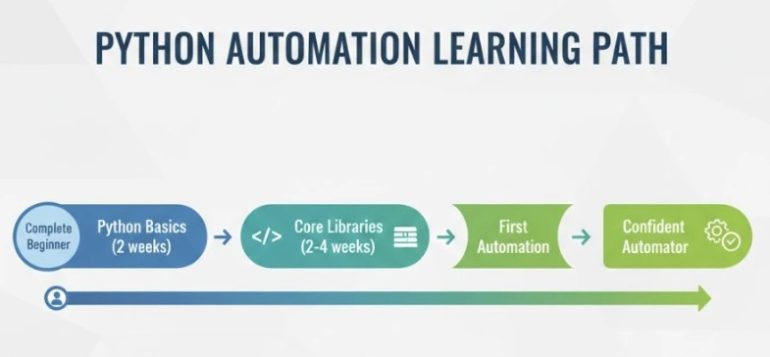
The Only Skills You Actually Need
Stop trying to learn everything. For Python automation specifically, focus here:
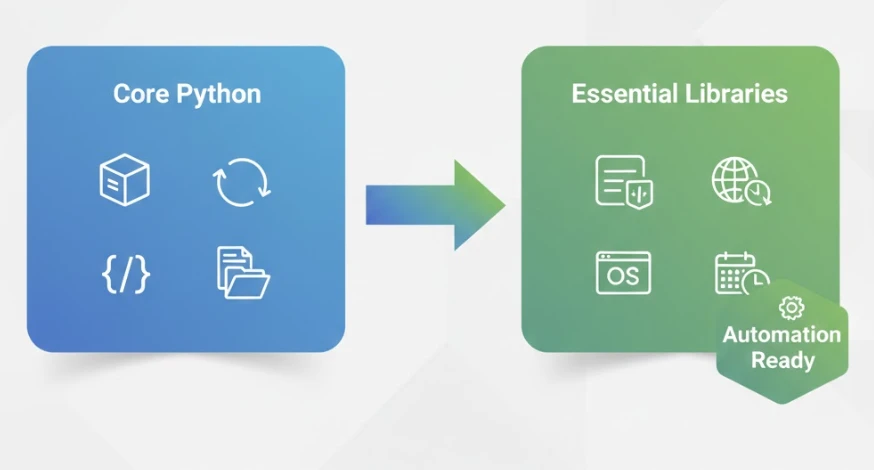
Core Python (2 weeks)
- Variables and data types — storing and manipulating information
- Lists and dictionaries — organizing multiple pieces of data
- Loops — doing something repeatedly (the heart of automation)
- Conditionals — making decisions in code
- Functions — packaging code for reuse
- File handling — reading and writing files
That’s it for core Python. Master these six concepts and you’re ready to automate.
Essential Libraries (2-4 weeks)
- Pandas — data manipulation powerhouse, handles Excel/CSV like magic
- Requests — talks to web APIs and services
- OS/Pathlib — file system operations
- Datetime — working with dates and times
Four libraries. Combined with core Python, these handle the vast majority of automation tasks. Everything else is optional specialization you can add later.
The Learning Approach That Works
How you learn matters as much as what you learn. These principles accelerate progress:
Code daily, even briefly. Fifteen focused minutes daily beats three-hour weekend sessions. Your brain builds programming intuition through consistent exposure, not occasional cramming.
Type code, don’t copy-paste. Physically typing reinforces syntax and structure. It feels slower but dramatically improves retention.
Break things intentionally. Modify working code to see what happens. Remove a line. Change a value. Understanding why errors occur builds debugging skills faster than only following working examples.
Apply immediately to real tasks. After learning any concept, find something in your actual work or life to apply it to. This contextual learning cements knowledge far better than abstract exercises.
Embrace confusion temporarily. Feeling lost is part of learning. Struggle with a problem for 20-30 minutes before seeking help. That struggle is when real learning happens.
Common Mistakes That Slow Learners Down
Avoid these traps that catch most beginners:
Tutorial paralysis: Watching course after course without building anything. After learning basics, every hour should include hands-on coding, not just watching.
Perfectionism: Refusing to run code until it’s “perfect.” Write ugly code that works first. Improve it later. Working ugly code teaches more than perfect code never written.
Learning too broadly: Trying to learn web development, data science, and automation simultaneously. Pick one path, go deep, then expand.
Avoiding errors: Treating error messages as failures instead of learning opportunities. Every error teaches something. Debugging is a core skill, not a sign of incompetence.
Going solo too long: Struggling for hours on problems that others have solved. Use forums, communities, and documentation. Knowing how to find answers is itself a crucial skill.
What Makes Structured Learning Different
Self-teaching Python is possible but inefficient. Here’s why structured courses accelerate progress:
Sequenced curriculum: Concepts build on each other in the right order. No jumping ahead to topics you’re not ready for, no wasting time on things you don’t need yet.
Curated content: Someone already filtered out outdated tutorials, incorrect information, and tangential topics. You learn what’s relevant, not what’s popular.
Progressive projects: Each project applies new skills to realistic scenarios. You build a portfolio while learning, not after.
Accountability structure: Deadlines, progress tracking, and completion goals keep you moving when motivation dips.
Community and support: Stuck on a problem? Someone who’s seen it before can unstick you in minutes instead of hours.
The time saved by structured learning often exceeds the course investment within weeks. Wandering through random tutorials for six months costs more than a focused course that gets you job-ready in two.
Your First Week: A Practical Start
Want to test if Python automation is for you? Here’s a concrete first week:
Day 1-2: Install Python, write your first script that prints text. Modify it. Break it. Fix it.
Day 3-4: Learn variables and basic operations. Write a script that calculates something useful to you.
Day 5-6: Understand lists and loops. Write a script that processes a list of items automatically.
Day 7: Combine what you’ve learned. Build a tiny automation — even just renaming files or organizing downloads.
By week’s end, you’ll know whether Python clicks for you. Most people discover it’s far more approachable than expected.
From Learning to Earning
Python automation skills translate directly to career value:
Immediate job impact: Automate tasks in your current role. This visibility leads to recognition, raises, and promotions.
New role opportunities: Automation specialist, data analyst, operations engineer — positions that weren’t accessible before.
Freelance potential: Businesses pay $50-$150/hour for automation consulting. Even part-time freelancing adds meaningful income.
Future-proofing: As AI transforms work, those who can build and manage automated systems remain valuable. Those doing work that should be automated don’t.
Start Today, Not Someday
Every week you postpone is another week of manual work that could be automated. Another week watching others advance with skills you could have. The best time to start was months ago. The second best time is now.
Python automation is learnable by anyone willing to put in consistent effort. The path is clear. The resources exist. The only variable is whether you begin.
Ready for the fastest path from beginner to automating real tasks? The Python Automation Course gives you exactly what you need — structured lessons, hands-on projects, and support — without the confusion of piecing together random tutorials. Join thousands who’ve transformed their productivity and careers through focused Python automation training.
